How Is Cell Division Important For Replacement And Repair
Where Exercise Cells Come From?
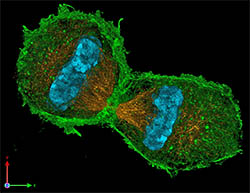
3D epitome of a mouse prison cell in the final stages of cell segmentation (telophase). (Image by Lothar Schermelleh)
Sometimes you lot accidentally bite your lip or skin your human knee, only in a thing of days the wound heals. Is it magic? Or, is there another explanation?
Every mean solar day, every hr, every second ane of the most important events in life is going on in your trunk—cells are dividing. When cells split up, they make new cells. A single cell divides to make 2 cells and these two cells then dissever to make 4 cells, and so on. We phone call this process "cell segmentation" and "cell reproduction," because new cells are formed when former cells divide. The ability of cells to divide is unique for living organisms.
Why Do Cells Divide?
Cells divide for many reasons. For example, when you skin your knee, cells divide to supplant old, dead, or damaged cells. Cells also split up so living things can grow. When organisms grow, it isn't because cells are getting larger. Organisms abound considering cells are dividing to produce more and more cells. In human bodies, nearly ii trillion cells split every day.
Watch cells divide in this fourth dimension lapse video of an animal cell (acme) and an E. coli leaner cell (bottom). The video compresses 30 hours of mitotic cell division into a few seconds. (Video past the National Institute of Genetics)
How Many Cells Are in Your Body?
You and I began equally a single prison cell, or what you would call an egg. Past the time you are an developed, you volition have trillions of cells. That number depends on the size of the person, but biologists put that number around 37 trillion cells. Yes, that is trillion with a "T."
How Do Cells Know When to Split up?
In cell segmentation, the cell that is dividing is chosen the "parent" jail cell. The parent jail cell divides into two "daughter" cells. The process so repeats in what is chosen the cell cycle.
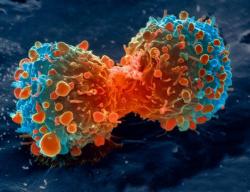
Jail cell division of malignant lung cell (Image from NIH)
Cells regulate their partitioning by communicating with each other using chemical signals from special proteins called cyclins. These signals human action like switches to tell cells when to starting time dividing and subsequently when to stop dividing. Information technology is important for cells to split up so you tin can grow then your cuts heal. It is as well important for cells to end dividing at the right time. If a cell can not end dividing when it is supposed to stop, this can lead to a disease called cancer.
Some cells, like pare cells, are constantly dividing. We demand to continuously make new pare cells to supervene upon the skin cells we lose. Did you know we lose 30,000 to 40,000 dead pare cells every infinitesimal? That ways nosotros lose effectually 50 million cells every twenty-four hour period. This is a lot of skin cells to replace, making prison cell segmentation in skin cells is and so important. Other cells, like nerve and encephalon cells, divide much less ofttimes.
How Cells Dissever
Depending on the blazon of prison cell, there are two ways cells dissever—mitosis and meiosis. Each of these methods of cell sectionalization has special characteristics. One of the key differences in mitosis is a single prison cell divides into two cells that are replicas of each other and have the same number of chromosomes. This type of cell partition is good for basic growth, repair, and maintenance. In meiosis a cell divides into four cells that take half the number of chromosomes. Reducing the number of chromosomes by one-half is important for sexual reproduction and provides for genetic variety.
Mitosis Prison cell Division
Mitosis is how somatic—or non-reproductive cells—divide. Somatic cells make up most of your body's tissues and organs, including peel, muscles, lungs, gut, and hair cells. Reproductive cells (like eggs) are non somatic cells.
In mitosis, the important affair to call up is that the daughter cells each have the same chromosomes and Deoxyribonucleic acid as the parent prison cell. The daughter cells from mitosis are called diploid cells. Diploid cells accept two complete sets of chromosomes. Since the daughter cells have exact copies of their parent cell's Dna, no genetic diversity is created through mitosis in normal good for you cells.
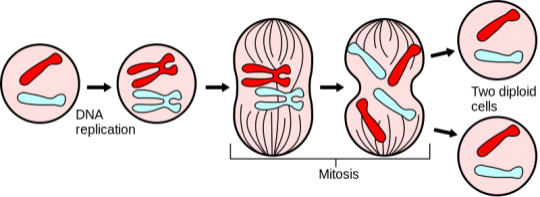
Mitosis cell division creates two genetically identical girl diploid cells. The major steps of mitosis are shown here. (Image by Mysid from Science Primer and National Eye for Biotechnology Information)
The Mitosis Cell Cycle
Before a cell starts dividing, it is in the "Interphase." It seems that cells must be constantly dividing (remember there are 2 trillion cell divisions in your trunk every day), only each cell actually spends most of its fourth dimension in the interphase. Interphase is the period when a cell is getting ready to split and beginning the cell cycle. During this time, cells are gathering nutrients and free energy. The parent cell is also making a re-create of its DNA to share as between the ii daughter cells.
The mitosis division process has several steps or phases of the cell bike—interphase, prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, and cytokinesis—to successfully make the new diploid cells.
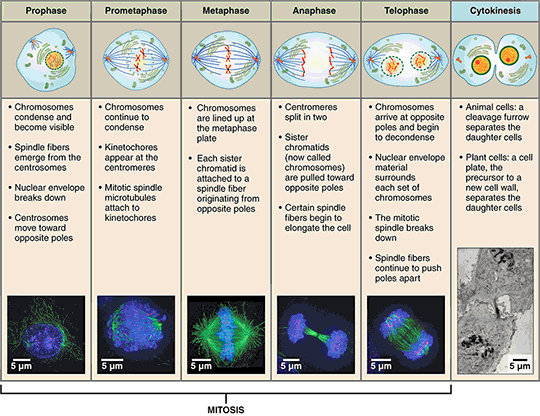
The mitosis prison cell cycle includes several phases that result in two new diploid daughter cells. Each stage is highlighted here and shown by lite microscopy with fluorescence. Click on the paradigm to larn more about each phase. (Image from OpenStax College with modified piece of work by Mariana Ruiz Villareal, Roy van Heesheen, and the Wadsworth Center.)
When a cell divides during mitosis, some organelles are divided between the 2 daughter cells. For case, mitochondria are capable of growing and dividing during the interphase, so the girl cells each have plenty mitochondria. The Golgi appliance, nonetheless, breaks down before mitosis and reassembles in each of the new daughter cells. Many of the specifics nearly what happens to organelles before, during and after cell division are currently being researched. (You can read more nearly cell parts and organelles past clicking here.)
Meiosis Cell Partition
Meiosis is the other main mode cells divide. Meiosis is cell sectionalization that creates sexual practice cells, like female egg cells or male sperm cells. What is important to remember almost meiosis? In meiosis, each new jail cell contains a unique set of genetic information. After meiosis, the sperm and egg cells can join to create a new organism.
Meiosis is why we have genetic variety in all sexually reproducing organisms. During meiosis, a modest portion of each chromosome breaks off and reattaches to another chromosome. This process is called "crossing over" or "genetic recombination." Genetic recombination is the reason full siblings made from egg and sperm cells from the same 2 parents can await very different from one some other.
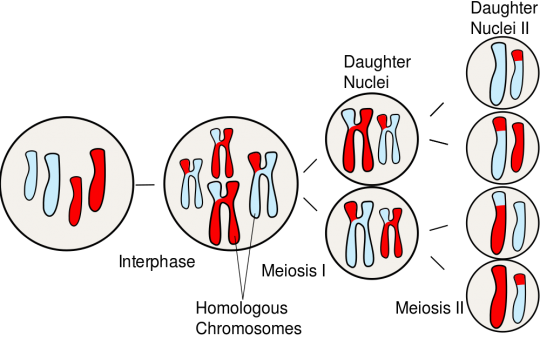
The meiosis cell cycle has ii main stages of segmentation -- Meiosis I and Meiosis II. The cease effect of meiosis is four haploid daughter cells that each incorporate different genetic information from each other and the parent prison cell. Click for more detail. (Image from Science Primer from the National Center for Biotechnology Data.)
The Meiosis Prison cell Cycle
Meiosis has two cycles of prison cell division, conveniently called Meiosis I and Meiosis II. Meiosis I halves the number of chromosomes and is also when crossing over happens. Meiosis II halves the amount of genetic data in each chromosome of each jail cell. The cease issue is four daughter cells called haploid cells. Haploid cells just have i set of chromosomes - one-half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
Before meiosis I starts, the prison cell goes through interphase. Only similar in mitosis, the parent cell uses this time to prepare for jail cell division past gathering nutrients and energy and making a copy of its Deoxyribonucleic acid. During the next stages of meiosis, this DNA will be switched around during genetic recombination and then divided between iv haploid cells.
And so remember, Mitosis is what helps the states abound and Meiosis is why nosotros are all unique!
References:
Bianconi Eastward, Piovesan A, Facchin F, Beraudi A, Casadei R, Frabetti F, Vitale Fifty, Pelleri MC, Tassani S, Piva F, Perez-Amodio S, Strippoli P, Canaider Due south. Ann. An estimation of the number of cells in the man body. Retrieved March 14, 2022 from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23829164.
Original brute cell and Eastward. Coli cell video from National Constitute of Genetics via Wikimedia. https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Movie_4._Cell_division.ogv
How Is Cell Division Important For Replacement And Repair,
Source: https://askabiologist.asu.edu/cell-division
Posted by: jacksonrometh.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How Is Cell Division Important For Replacement And Repair"
Post a Comment